Deploy Nuxt on a cloud provider
Vercel
You can use the Vercel Marketplace to add compatible storage to your project (Postgres, Turso, Redis, Vercel Blob, etc.).
Cloudflare
You can deploy your project on your own Cloudflare account, you need to create the necessary resources in your account and configure your project to use them (D1, KV, R2, etc.).
hub config.Configure Bindings
NuxtHub auto-generates the wrangler.json file at build time when you provide resource IDs in your config. No manual wrangler.jsonc is required.
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
// D1 database
db: {
dialect: 'sqlite',
driver: 'd1',
connection: { databaseId: '<database-id>' }
},
// KV namespace (binding defaults to 'KV')
kv: {
driver: 'cloudflare-kv-binding',
namespaceId: '<kv-namespace-id>'
},
// Cache KV namespace (binding defaults to 'CACHE')
cache: {
driver: 'cloudflare-kv-binding',
namespaceId: '<cache-namespace-id>'
},
// R2 bucket (binding defaults to 'BLOB')
blob: {
driver: 'cloudflare-r2',
bucketName: '<bucket-name>'
}
}
})
wrangler.toml file.Config Mapping Reference
The following table shows how NuxtHub configuration options map to Wrangler configuration:
| NuxtHub Config | Wrangler Key | Generated Value |
|---|---|---|
hub.db.connection.databaseId | d1_databases[].database_id | From config |
| - | d1_databases[].binding | DB (hardcoded) |
hub.kv.namespaceId | kv_namespaces[].id | From config |
hub.kv.binding | kv_namespaces[].binding | KV (default) |
hub.cache.namespaceId | kv_namespaces[].id | From config |
hub.cache.binding | kv_namespaces[].binding | CACHE (default) |
hub.blob.bucketName | r2_buckets[].bucket_name | From config |
hub.blob.binding | r2_buckets[].binding | BLOB (default) |
Environment Resolution
During the build process, NuxtHub resolves the target environment using the following steps:
- Checks the
CLOUDFLARE_ENVenvironment variable - If set, merges environment-specific configuration from
wrangler.jsonc - Generates
.output/server/wrangler.jsonwith the resolved bindings - Wrangler uses this configuration during deployment
Deploy
Create a Cloudflare Workers project and link your GitHub or GitLab repository. NuxtHub auto-configures bindings from your nuxt.config.ts during build.
migrations_table and migrations_dir in .output/server/wrangler.json. This enables Wrangler-managed migrations, but wrangler deploy and Cloudflare Git / Workers Builds do not apply D1 migrations automatically. Run a separate migration step before deploy.You can also create a wrangler.jsonc file manually in the root of your project:
{
"$schema": "node_modules/wrangler/config-schema.json",
// D1 database
"d1_databases": [
{ "binding": "DB", "database_name": "<name>", "database_id": "<id>" }
],
// R2 bucket
"r2_buckets": [
{ "binding": "BLOB", "bucket_name": "<bucket-name>" }
],
// KV namespaces
"kv_namespaces": [
{ "binding": "KV", "id": "<kv-namespace-id>" },
{ "binding": "CACHE", "id": "<cache-namespace-id>" }
]
}
Environments
Wrangler supports environments to manage different configurations for staging, preview, or other deployment targets. You can define environment-specific bindings in your wrangler.jsonc:
{
"$schema": "node_modules/wrangler/config-schema.json",
// Production bindings (top-level)
"d1_databases": [
{
"binding": "DB",
"database_id": "<production-database-id>"
}
],
// Preview environment
"env": {
"preview": {
"d1_databases": [
{
"binding": "DB",
"database_id": "<preview-database-id>"
}
]
}
}
}
To deploy to a specific environment, set the CLOUDFLARE_ENV environment variable during build:
CLOUDFLARE_ENV=preview nuxt build
Non-Inheritable Keys
The following bindings do not inherit from the top-level configuration and must be specified explicitly in each environment:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
d1_databases | D1 database bindings |
kv_namespaces | KV namespace bindings |
r2_buckets | R2 bucket bindings |
vars | Environment variables |
durable_objects | Durable Object bindings |
services | Service bindings |
undefined at runtime. This does not produce an error during deployment, which can lead to unexpected behavior in production.Cache
When self-hosting and using devtools for cache management (viewing/deleting cache entries), you need to configure additional environment variables:
In your Cloudflare project, go to Settings → Environment Variables and add:
Workers Builds
If deploying to Cloudflare Workers, you can use Workers Builds to automatically deploy your project on every commit.
Pages CI
If deploying to Cloudflare Pages, you can use Pages CI to automatically deploy your project on every commit.
NuxtHub Admin (Deprecated)
The NuxtHub Admin is made to simplify your experience with NuxtHub, enabling you to effortlessly manage teams and projects, as well as deploying NuxtHub application with zero-configuration on your Cloudflare account.
Production vs Preview Deployments
NuxtHub supports two types of deployments: production and preview.
Production Deployments
- When setting up your project, you can specify a production branch (defaults to
main) - Successful deployments to the production branch will be:
- Accessible via your primary domain
- Also available at
<commit>.<project>.pages.dev
Preview Deployments
- Any deployment from a non-production branch (including pull requests) is considered a preview
- Successful preview deployments are accessible via:
<commit>.<project>.pages.dev<branch>.<project>.pages.dev
NuxtHub CLI (Deprecated)
Deploy your local project with a single command:
npx nuxthub deploy
The command will:
- Ensure you are logged in on admin.hub.nuxt.com
- Make sure you linked your Cloudflare account
- Link your local project with a NuxtHub project or help you create a new one
- Build your Nuxt project with the correct preset
- Deploy it to your Cloudflare account with all the necessary resources (D1, KV, R2, etc.)
- Provide you with a URL to access your project with a free
<my-app>.nuxt.devdomain
npm i -g nuxthub.Usage with CI/CD
nuxthub deploy command is designed to run non-interactively in CI/CD environments. It won’t prompt for additional input (such as logging in or linking the project). As long as the required environment variables are set, deployment will proceed automatically.To integrate the nuxthub deploy command within your CI/CD pipeline, set the following environment variables:
NUXT_HUB_PROJECT_KEY– Your project key available in:- Your project settings in the NuxtHub Admin
- Your
.envfile (if you rannpx nuxthub link)
NUXT_HUB_USER_TOKEN– Your personal token, available in User settings → Tokens in the NuxtHub Admin
Example command:
NUXT_HUB_PROJECT_KEY=<my-project-key> NUXT_HUB_USER_TOKEN=<my-user-token> npx nuxthub deploy
This will authenticate your user and link your NuxtHub project for deployment.
GitHub Action (Deprecated)
After linking a GitHub repository to your project, NuxtHub automatically adds a GitHub Actions workflow to automatically deploy your application on every commit using the NuxtHub GitHub Action.
NuxtHub integrates with GitHub deployments. This allows you to:
- View deployment statuses within GitHub
- Setup deployment concurrency
- Require approvals for deploying to environments
After deploying from a pull request, NuxtHub automatically adds a comment with information about the deployment.
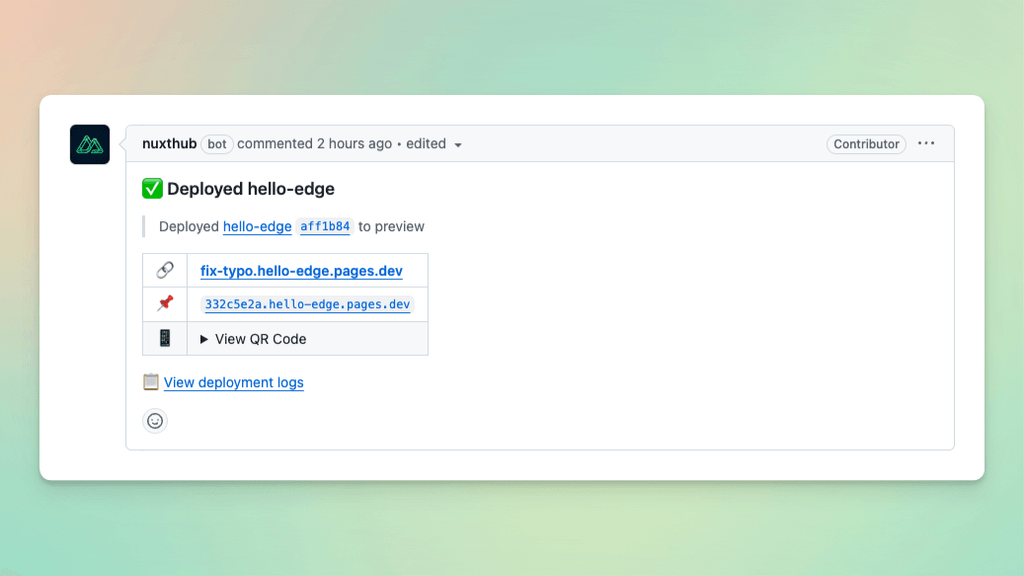
Default workflow
The GitHub Workflow added to your repository is automatically tailored to your project's package manager. This is an example of a workflow added for a project using pnpm.
We support pnpm, yarn, npm and Corepack. If you use a different package manager, you can customise the generated nuxthub.yml GitHub Action.
name: Deploy to NuxtHub
on: push
jobs:
deploy:
name: "Deploy to NuxtHub"
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
id-token: write
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install pnpm
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v4
with:
version: 10
- name: Install Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 24
cache: 'pnpm'
- name: Install dependencies
run: pnpm install
- name: Build & Deploy to NuxtHub
uses: nuxt-hub/action@v2
Options
Inputs
The following input parameters can be provided to the GitHub Action. Learn more about Workflow syntax for GitHub Actions on GitHub's documentation.
directory.Outputs
The GitHub Action provides the following outputs that you can use in subsequent workflow steps.
- https://example.nuxt.dev (main)
- https://abcdefg.example.pages.dev (feat/example)
- https://example.nuxt.dev (main)
- https://feat-example.example.pages.dev (feat/example)
- https://hello-world-staging.example.workers.dev ('staging' environment)
Environment Variables & Secrets
The NuxtHub GitHub Action builds the Nuxt application using build-time environment variables and secrets specified within NuxtHub Admin.
NUXT_UI_PRO_LICENSE.Setup
Creating a new project
When creating a new project from a template, or importing a Git repository, the GitHub Action workflow will automatically be set up for you.
Linking a repository to existing projects
Link your project to a GitHub repository within NuxtHub Admin → Projects → <Your Project> → Settings → General → Git Repository
Migration from Cloudflare CI to GitHub Actions
Migrate your project to GitHub Actions within NuxtHub Admin → Projects → <Your Project> → Settings → General → Git Repository → Begin Migration.
Monorepo setup
Our GitHub integration supports deploying multiple applications from the same repository.
When linking a Git repository, set "project root directory" to the base folder of your Nuxt application corresponding to that NuxtHub project.
When a repository is already linked to at least one project, additional projects linked will have the generated GitHub Actions workflow named nuxthub-<projectSlug>.yml.
project-key input parameter must be specified on each Deploy to NuxtHub GitHub Action.Current limitations
- Separate applications should be deployed using different workflow jobs.
GitLab CI (Deprecated)
This section will guide you to implement the GitLab CI.
The integration with GitLab CI builds on the Usage with CI/CD section,
make sure you have those two variables NUXT_HUB_PROJECT_KEY and NUXT_HUB_USER_TOKEN.
User Token Variable
- Open your Repository (on GitLab) > Settings > CI/CD > Variables
- Click on Add variable
- Set Visibility to Masked and hidden
- Remove protected Flag (since we may use this variable also on non-protected branches)
- Give a Key name =
NUXT_HUB_USER_TOKEN - Paste your
NUXT_HUB_USER_TOKEN— Your personal token, available in User settings → Tokens in the NuxtHub Admin - Click Add variable
NUXT_HUB_PROJECT_KEY is used later in Configure Projects for GitLab.Project Configuration
- Create a
.gitlab-ci.ymlin your repository root - Paste the following configuration
# if one job fails, pipeline should fail
workflow:
auto_cancel:
on_job_failure: all
variables:
APP_PATH: "PATH/TO/YOUR/APP"
NUXT_HUB_PROJECT_KEY: "YOUR_NUXT_HUB_PROJECT_KEY"
# add additional steps as needed
stages:
- deploy
- callback
deploy_project:
stage: deploy
# here we use Bun, you can change this.
image: "oven/bun:slim"
script:
- echo "Deploying project_a app..."
- cd $APP_PATH
# you can not use node_modules from cache, since nuxthub needs write access
- bun install
# if you set up your variables correctly this should deploy successfully
- bunx nuxthub deploy
rules:
# here we configure auto deploy on branch: staging and main
- if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "staging" || $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "main"'
manual_deploy_project:
stage: deploy
image: "oven/bun:slim"
when: manual
script:
- echo "Deploying project_a app..."
- cd $APP_PATH
- bun install
- bunx nuxthub deploy
callback:
stage: callback
script:
- echo "Deploy reached."
./apps/project-foo/.gitlab-ci.yml). Then follow the Monorepo Setup section.callback job is needed to mark the pipeline as successfully,
especially if deploy_project has not run. You can avoid this by setting
allow-failure: true but this will result in other drawbacks.
Or simply deploy on every branch, which results in more traffic.preview.Monorepo Setup
If you have a monorepo with multiple apps (e.g. ./apps/project-foo), then we make sure our pipelines can run parallel.
- Create in your repository root a
.gitlab-ci.yml - Paste the following configuration
# if one job fails, pipeline should fail
workflow:
auto_cancel:
on_job_failure: all
stages:
- trigger_apps
trigger_project_a:
stage: trigger_apps
rules:
- changes:
- "apps/project-foo/**/*"
trigger:
strategy: depend
include:
- local: "apps/project-foo/.gitlab-ci.yml"
trigger_project_b:
stage: trigger_apps
rules:
- changes:
- "apps/project-bar/**/*"
trigger:
strategy: depend
include:
- local: "apps/project-bar/.gitlab-ci.yml"
add_manual_triggers:
stage: trigger_apps
trigger:
strategy: depend
include:
- local: ".manual-triggers.yml"
This configuration separates your main pipeline from child pipelines, each project (app) has its own .gitlab-ci.yml Those child pipelines are only triggered if changes are made in their app folder.
Sometimes GitLab changes are not recognized (previous pipeline failed and new push has no changes in app folder), for that case, you can add manual triggers for the child pipelines by adding a .manual-triggers.yml in the project root.
workflow:
auto_cancel:
on_job_failure: all
stages:
- trigger_apps
- callback
trigger_project_a:
stage: trigger_apps
when: manual
trigger:
strategy: depend
include:
- local: "apps/project-foo/.gitlab-ci.yml"
trigger_project_b:
stage: trigger_apps
when: manual
trigger:
strategy: depend
include:
- local: "apps/project-bar/.gitlab-ci.yml"
callback:
stage: callback
script:
- echo "manual triggers set"
depends and workflow.auto_cancel.on_job_failure: all a pipeline is failed, if one job fails.
This assures a clean main / staging branch. Change it to your needs.